Thermal runaway is a chain reaction that can be extremely challenging to halt once initiated inside a battery cell. During thermal runaway, the temperature of the battery cell increases rapidly, which can lead even to battery explosions. This phenomenon can be triggered by internal short circuits caused by battery damage, inadequate maintenance, overcharging, or rapid recharging.
The uncontrolled combustion of batteries poses a potential threat to operators of high-performance batteries, especially electric vehicle drivers, because the speed at which the battery catches fire is so fast, that a burning EV's driver or passengers sometimes do not get a chance to exit from their vehicle.
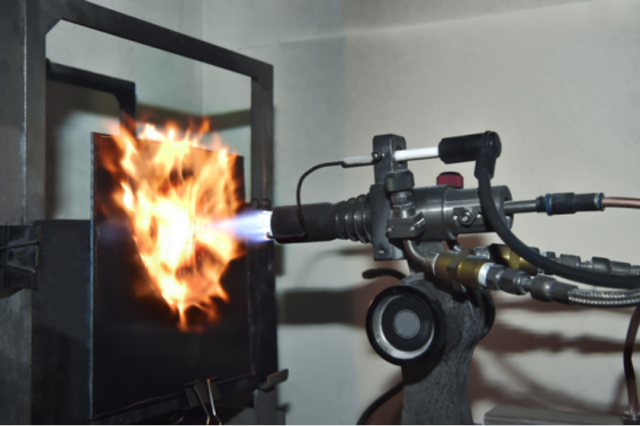
LG Chem said in a statement the company has worked with domestic automotive material producer LX Hausys to develop the flame-resistant material. When the 1.6-millimeter-thin Special Flame Retardant CFT was exposed to temperatures more than 1,500 degrees Celsius, it displayed no signs of melting, dripping, or hole formation for longer than 20 minutes. LG Chem said the material with higher durability than conventional thermoplastics can be used for the top and bottom covers of large battery packs.
"We have been working closely with LX Hausys since we developed and announced a super flame barrier material last year," LG Chem's engineering materials' marketing division head Tom Shin said in a statement on October 27. The company said LX Hausys has increased the flame barrier material's performance through a manufacturing technology that involves layering the material with tape.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.