[Courtesy of LG Uplus]
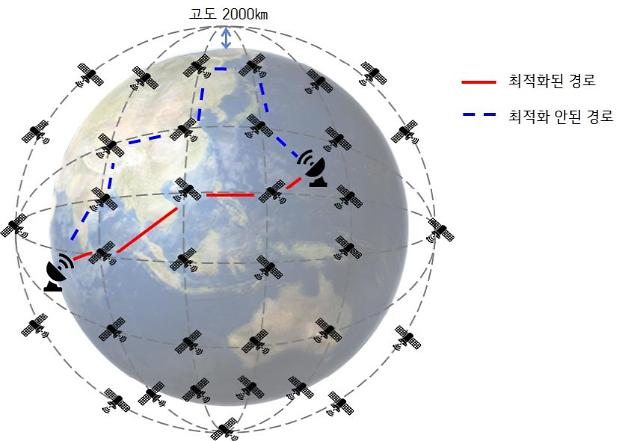
LG Uplus (LGU+) said that researchers have used a quantum computer commercialized by D-Wave Systems, a Canadian quantum computing company, to quickly calculate the number and distance of surrounding satellites that can communicate from one satellite.
Low-earth orbit satellites change their positions in real time and need to find their optimal network configuration in a short time. Networks must be reconfigured from time to time if satellites approach a distance where communication is possible. Since the number of data transmission paths increases in proportion to the number of nodes, network optimization is required to find the fastest path.
In their joint research for six months that began in December 2021, researchers from LGU+ and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) found that services that are not different from ground communication can be implemented even in satellite communication environments through network optimization algorithms.
"We will provide optimal communication quality for satellite communication through quantum computers, which are key technologies in the future," Lee Sang-heon, head of LGU+'s advanced network technology research unit, said in a statement on June 14. "We will lead research on advanced technologies ahead of the upcoming 6G era and give outstanding experiences to our customers."
Researchers believe that satellite communication will become important to achieve "superspace." LGU+ predicted that if optimized satellite communication is commercialized, superspace can be realized to connect communication to objects that travel at a maximum speed of 1,000 kilometers (621 miles) per hour.
As a frontrunner in disseminating 5G mobile services, South Korea aims to achieve the world's first commercialization of 6G mobile telecommunication in 2028.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.



