[Yonhap Photo]
South Korea has been the leading country in the world's liquid crystal display (LCD) and organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display market for 17 years until China became the top country in sales in 2021. Chinese display makers targeted the global market with cheaper LCD display units that have a similar performance to that of displays made by South Korean companies like Samsung Display and LG Display.
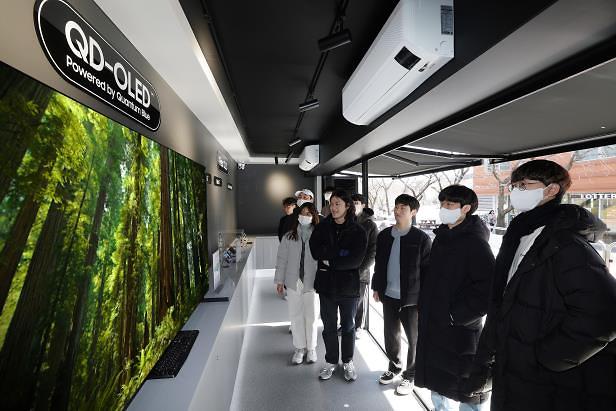
OLED display products are more expensive than LCD counterparts, and they are adopted by premium electronic devices like luxury television units or laptops and computer monitors for professionals as OLEDs have the ability to display a more accurate spectrum of light and more vivid colors. OLED display panels are normally paper-thin and can be created into foldable and flexible displays. OLED is slowly gaining ground in the global smartphone market with more than 40 percent market share.
Samsung Display held a ceremony at the company's campus in Asan some 90 kilometers (55 miles) south of Seoul on April 4 and said that a new OLED display factory will be built by 2026. The ceremony was attended by South Korean President Yoon Seok-yeol, Samsung Electronics Executive Chairman Jay Y. Lee, Samsung Display President Choi Joo-sun, and some other 200 guests.
According to the flat panel maker, the 8.6th-generation OLED panels are more cost-effective and productive. The current sixth-generation panel can create 32 14-inch displays while the 8.6th-generation panel would be able to manufacture up to 88 14-inch displays.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.