SEOUL, November 26 (AJP) - South Koreans have emerged as the world's most avid ChatGPT users, spending more time on the AI platform than on the country's dominant portal Naver, and pushing Korea to become OpenAI's second-most profitable market despite its small population, data showed.
According to app analytics firm Sensor Tower, Korea ranked No. 2 after the United States in ChatGPT revenue contribution. Global downloads of the ChatGPT app have surpassed 1.4 billion, with India accounting for the largest share at 15.7 percent.
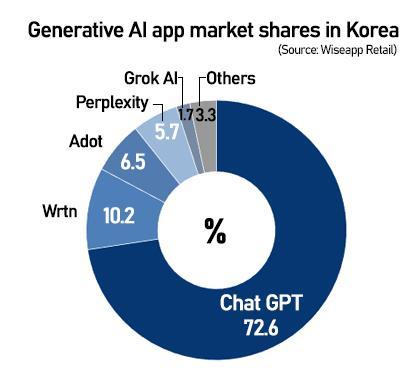
Korea represented a modest 1.5 percent of total downloads, placing it 21st — but contributed a disproportionately high 5.4 percent of global revenue, or roughly $200 million, out of ChatGPT's $3.5 billion worldwide.
Korea's revenue per download reached $8.7 — nearly on par with the U.S. at $8.8 — indicating an unusually high share of paid subscribers. The service's explosive rise in Korea accelerated after OpenAI introduced image-generation features that allow users to transform portraits into Ghibli-style or other customized illustrations in seconds.
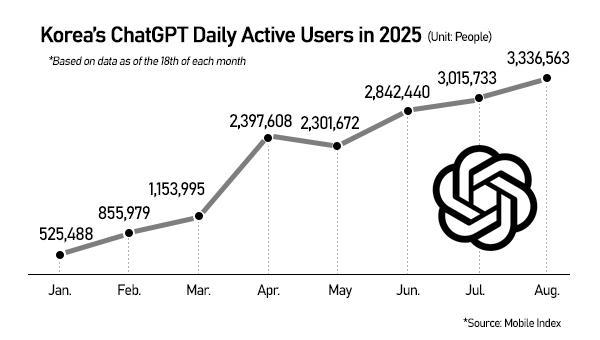
App downloads hit a record in August, and revenue peaked again in October. From Jan. 1 to Nov. 20, ChatGPT ranked No. 1 in overall downloads and No. 4 in app revenue in Korea — an exceptional feat in a market where the top-grossing apps are typically mobile games. ChatGPT also dominated Korea's AI-assistant category. Downloads were three times those of Google's Gemini, daily active users were eight times higher, and revenue exceeded that of Anthropic's Claude by more than tenfold.
On the web, ChatGPT ranked as the fifth most-visited site in Korea — trailing only YouTube, Naver, Google and Daum. Korean users spent an average of 367 minutes per month on the site, about 1.7 times longer than on Naver. Roughly 90 percent of visits came from users typing the address directly rather than arriving via search, suggesting ChatGPT has already become a primary work tool rather than a supplemental service.
The broader uptake of AI services in South Korea has also surged. A March report by the Ministry of Science and ICT showed generative AI usage among the general population doubled from 17.6 percent in 2023 to 33.3 percent in 2024.
Overall AI service use — spanning translation tools, voice recognition and recommendation systems — climbed from 32.4 percent in 2021 to 60.3 percent last year. Most users relied on AI for information searches, document writing, translation and other productivity tasks.
Digital consumption patterns are shifting in parallel. Subscription-based online services jumped from 13.1 percent to 49.4 percent in one year, while overseas e-commerce usage — led by AliExpress and Temu — rose from 20 percent to 34.3 percent as global platforms expanded their footprint in Korea.
A Science and ICT Ministry official said the government aims to "strengthen public digital skills and ensure the ethical use of AI," noting that further policy measures are in the works.
Workplace adoption is even more pronounced. A Bank of Korea survey of 5,512 workers conducted between May and June found that 63.5 percent had used generative AI at least once, and 51.8 percent had used it for work — roughly double the 26.5 percent reported in the United States. Heavy users — those spending more than an hour a day on AI tools — accounted for 78.6 percent in Korea, compared with just 31.8 percent in the U.S.
The Bank of Korea estimated that AI tools have reduced working hours by an average of 3.8 percent per week and may have contributed up to 1 percentage point to Korea's GDP growth since ChatGPT's launch in late 2022. The gains were strongest among highly educated workers and those with shorter job experience, as AI helped narrow skill gaps.
A central bank official cautioned, however, that shorter working hours do not always translate directly into higher output. "Actual productivity improvements may be smaller if the saved time is not used for additional work," the official said.
As AI becomes increasingly embedded in everyday life and professional workflows, analysts say generative AI is reshaping the architecture of Korea's digital-services market. Companies and government agencies are racing to upgrade their platforms, and Korea's rapid adoption curve is expected to leave a lasting imprint on the country's AI ecosystem.
Copyright ⓒ Aju Press All rights reserved.